Transformer,three phase:Potential Transformers
Potential Transformers
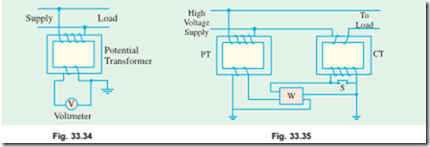
These transformers are extremely accurate-ratio step-down transformers and are used in conjunction with standard low-range voltmeters (usually 150-V) whose deflection when divided by voltage transformation ratio, gives the true voltage on the high voltage side. In general, they are of the shell-type and do not differ much from the ordinary two-winding transformers discussed so far, except that their power rating is extremely small. Upto voltages of 5,000, potential transformers are usually of the dry type, between 5,000 and 13,800 volts, they may be either dry type or oil immersed type, although for voltages above 13,800 they are always oil immersed type. Since their secondary windings are required to operate instruments or relays or pilot lights, their ratings are usually of 40 to 100 W. For safety, the secondary should be completely insulated from the high-voltage primary and should be, in addition, grounded for affording protection to the operator. Fig.
Fig. 33.35 shows the connections of instrument transformers to a wattmeter. While connecting the wattmeter, the relative polarities of the secondary terminals of the transformers with respect to their primary terminals must be known for connections of the instruments.




Comments
Post a Comment