Synchronous Motor:Power Developed by a Synchronous Motor
Power Developed by a Synchronous Motor
In Fig. 38.21, OA represents supply voltage/phase and Ia = I is the armature current, AB is back e.m.f. at a load angle of a. OB gives the resultant volt- age ER = IZS (or I XS if Ra is negligible). I leads V by f and lags behind ER by an angle q = tan (X S / Ra). Line CD is drawn at an angle of q to A B. AC and ED are ^ to CD (and hence to AE also).
Mechanical power per phase developed in the rotor is
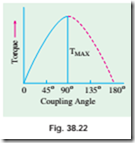
This shows that the maximum power and hence torque (∵ speed is constant) depends on V and Eb i.e., excitation. Maximum value of q (and hence a) is 90º. For all values of V and Eb, this limiting value of a is the same but maximum torque will be proportional to the maximum power developed as given in equation (iii). Equation (ii) is plotted in Fig. 38.22.
Alternative Expression for Power Developed







Comments
Post a Comment